Before I start, I would like to say a couple of things. First, is an apology. I am sorry for not being active and being so late with the last article (Sorry Sayantan and all those who have been waiting on this). Got entangled in some work. Secondly, it has been rightly pointed out to me by one @johnwitcher about the bug in Next Auth version 4.21.1. This bug causes the getCsrfToken() to resolve to undefined. The solution to this is to send headers of your request instead of the whole request object. The code with getCsrfToken() would thus become:
await getCsrfToken({ req: {headers: req.headers })
We use this in our mini-project during authentication for getting a nonce value for SIWE. That’s where this change needs to be included. The full solution to this can be found on this recent GitHub Issue and I would like to extend my thanks to the community member who pointed it out and to the devs who provided the solution.
Great! So now that we have that out of the way, let's get the show on the road for one last time in this series.
Housekeeping
The code discussed in this tutorial and the mini-project for this series is available at this GitHub Repo:
Now, when we last left off, we had created a hidden page, integrated Wagmi, WalletConnect v2 and sparingly used Viem. We had also integrated Next Auth with our NextJs 13 project in such a manner that Next Auth was being used in conjunction with WalletConnect v2 and SIWE (Sign-in with Ethereum). This is the last article in the series and in this one, we take the final step towards completing this mini-project.
In this article, we will modify our Authenticated/Hidden page and make it so that it can be used to interact with Smart contracts. For the purpose of this tutorial, I have deployed a simple Greeting Smart contract (which will serve as a simple example) and an NFT smart contract (example 2) beforehand on Polygon Mumbai Testnet. We will use Wagmi hooks to interact with these two contracts on Mumbai Testnet. The smart contracts are also available in the aforementioned repo. Towards the end of the tutorial, the hidden page will look something like the page shown below.
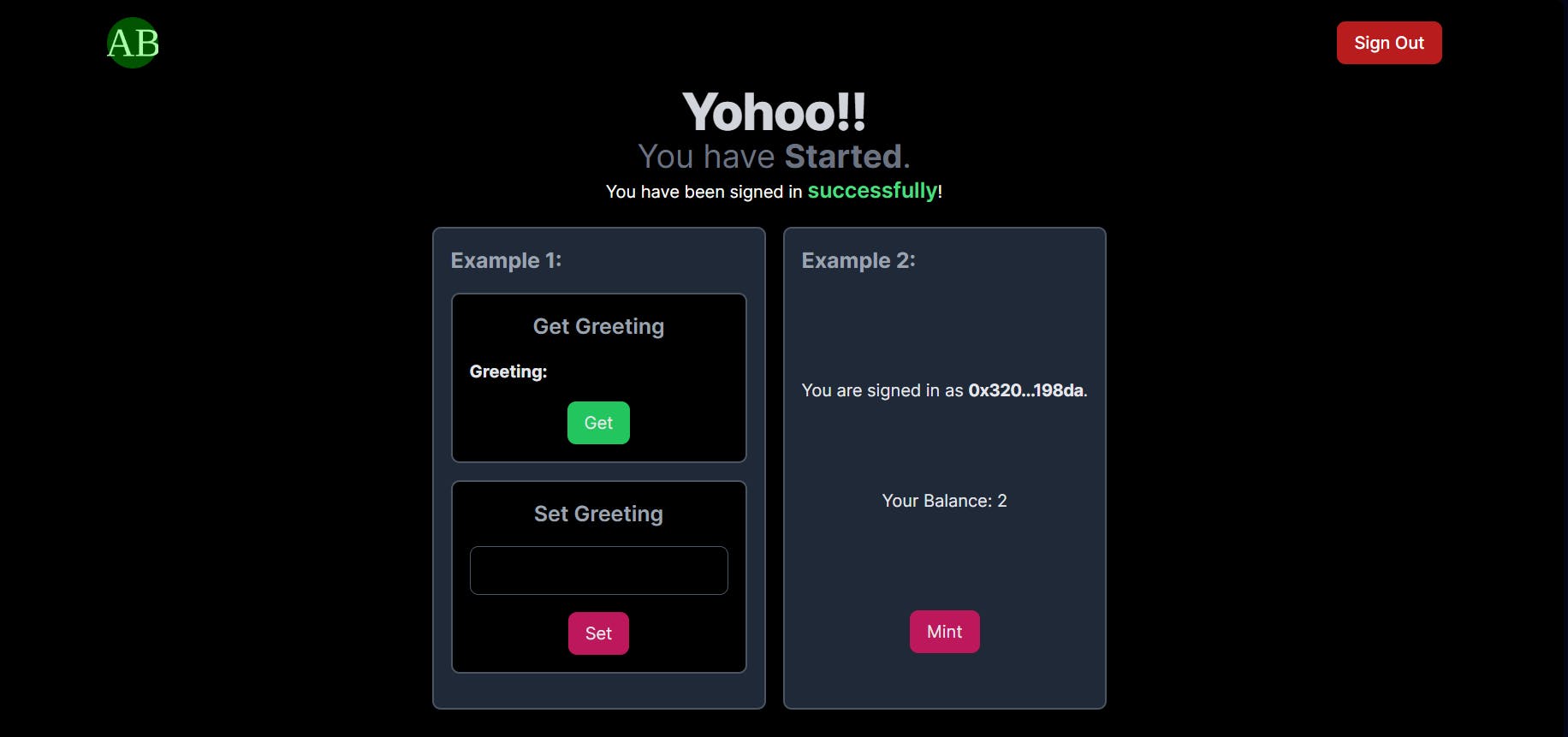
To that end, we will need to create a components directory inside app directory of our NextJs project. Now we will try to make sure that we can render on the server as much as possible. For the client-side rendered components, we will use Dynamic Modules in NextJs 13 to have lazy loading. Inside the components directory folder, create three more folders -example1, example2andui`.
We will store our reusable UI components in the ui folder. While the code for interacting with smart contracts will be in example1 and example2. Additionally, we will also need to create a folder called blockchain in the project root (at the same level as app folder). This is the folder where we will keep the ABIs of the deployed contracts.
The addresses of the deployed contracts will be stored in Environment variables called NEXT_PUBLIC_GREETING_CONTRACT and NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT. These will be of type 0x${string}. This is the type of string that Wagmi and Viem accept. We can have this conversion done while we use these variables in the Wagmi and Viem-related codes but because of our usage of additional-env.d.ts file, we can easily do it in one-step. This means we won’t have to use something like process.env. NEXT_PUBLIC_GREETING_CONTRACT as 0x${string} in our actual code. Our additional-env.d.ts file would thus look like this:
declare global {
namespace NodeJS {
interface ProcessEnv {
NODE_ENV: "development" | "production";
NEXT_PUBLIC_W3C_PID: string;
NEXT_PUBLIC_SIGNIN_MESSAGE: string;
NEXTAUTH_SECRET: string;
SIWE_DOMAIN: string;
NEXT_PUBLIC_GREETING_CONTRACT: `0x${string}`;
NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT: `0x${string}`;
}
}
}
// If this file has no import/export statements (i.e. is a script)
// convert it into a module by adding an empty export statement.
export {};
Make sure to add the env variables in your .env file as well. In our case, we need to place the .env file at the root of our frontend folder of the repo (GitHub repo mentioned above). We will take a bottom-up approach to build our project. We will create a layout for your card component, an encapsulated button component with our custom style, a sign-out button and then the examples. The final step would be putting it all together on the hidden page of our NextJs 13 project. This completes the housekeeping part and now we move to creating the UI parts.
Reusable UI Components
A Styled Button with Tailwind CSS
Since we are using many buttons in our mini-project, it is a good idea to create single-styled button components that would aggregate the CSS properties and allow us to customize them as well. This would prevent the use of overly long and repetitive class names. In our case, we use the code below to create a styled button.
'use client'
import React, { ButtonHTMLAttributes, ReactNode } from "react";
import cx from "classnames";
type StyledButtonProps = ButtonHTMLAttributes<HTMLButtonElement> & {
color: "red" | "green" | "blue" | "pink" | "yellow" | "violet";
children: ReactNode;
};
const StyledButton = ({
children,
color,
...otherProps
}: StyledButtonProps) => {
const colorClass =
color === "red"
? "bg-red-700 hover:border hover:border-red-700"
: color === "yellow"
? "bg-yellow-400 hover:border hover:border-orange-700"
: color === "violet"
? "bg-violet-700 hover:border hover:border-violet-700"
: color === "blue"
? "bg-blue-700 hover:border hover:border-blue-700"
: color === "green"
? "bg-green-500 hover:bg-green-800 hover:shadow-[0px_0px_15px_5px_green]"
: "bg-pink-700 hover:bg-pink-900 hover:border-none hover:shadow-[0px_0px_15px_5px_pink]";
return (
<button
className={cx("rounded-lg py-2 px-4 hover:bg-transparent", colorClass)}
{...otherProps}
>
{children}
</button>
);
};
export default StyledButton;
This code needs to go inside StyledButton.tsx inside ui folder. Most of the code above is React-specific. You shouldn’t have any problem understanding the above. But just for the sake of completeness let’s go over it once.
We make our button a client-component. Now in a production-grade project, I really prefer to have separate styled buttons – one for the server and another for the client. The Server rendered button components are for things like Form Submission actions and Links in NextJS 13. While the client-rendered ones I would use wherever a state-based interaction is needed.
Since this is a mini-project, I have just stuck with a single client-rendered button. Between lines 5-8, we define the props this button can expect. To make our lives easier, we merge this with the ButtonHTMLAttributes<HTMLButtonElement> props. This basically says – “expect anything a simple button component might take and also take in the props I define after the &”. Between lines 14 and 25, we just create a conditional class. This applies the color which is passed as props to this component. The classnames package is mighty helpful at line 28. It allows us to first define a class name which will be applied by default followed by the conditional ones.
Card Layout
Next Up, is the card component. The code below goes inside Card.tsx in the ui folder. Again, it's not any voodoo. It’s just plain React Code. We just make a container to house our examples. Notice that this component is server rendered unlike our button above. This helps us minimize the client-rendered parts and provides us with “Islands of Interactivity” – a term you would hear a lot with NextJs13 and frameworks like Astro.
import React, { ReactNode } from "react";
type CardPropsType = {
children: ReactNode;
};
const Card = ({ children }: CardPropsType) => {
return (
<div className=" mt-5 bg-gray-800 border-2 border-gray-600 p-4 rounded-lg w-1/3 min-w-max text-gray-200">
{children}
</div>
);
};
export default Card;
Non-Reusable UI Components
Sign-out Button
We abstract away the details of our sign-out logic to the SignoutButton placed inside the components directory. The logic itself is explained in the previous article. This allows for the button to be used wherever we want a way for the user to exit. In our case, we put it in the App bar discussed next.
"use client";
import { useDisconnect } from "wagmi";
import { signOut } from "next-auth/react";
import React from "react";
import StyledButton from "./ui/StyledButton";
const SignoutButton = () => {
const { disconnectAsync } = useDisconnect();
const handleSignout = async () => {
disconnectAsync();
signOut({ callbackUrl: "/" });
};
return (
<StyledButton color="red" onClick={handleSignout}>
Sign Out
</StyledButton>
);
};
export default SignoutButton;
The Code above contains the logic that uses Wagmi hook useDisconnect() and redirects the user back to the homepage. Since we need the on-click interaction here, we make this component a client component.
Simple Appbar with Tailwind
The Code below contains the styled appbar we are going to use in our project.
import React from "react";
import Image from "next/image";
import logo from "@/public/logo192.png"
import SignoutButton from "./SignoutButton";
const CustomAppbar = () => {
return (
<nav className="bg-none">
<div className="max-w-screen-xl flex flex-wrap items-center justify-between mx-auto p-4">
<a href="https://abhikbanerjee.com/" className="flex items-center">
<Image
src={logo}
className="h-12 w-12 mr-3 rounded-xl hover:shadow-[0px_0px_15px_5px_green]"
alt="Abhik Banerjee Logo"
/>
</a>
<div className="hidden w-full md:block md:w-auto" id="navbar-default">
<ul className="font-medium flex flex-col p-4 md:p-0 mt-4 border border-gray-100 rounded-lg bg-gray-50 md:flex-row md:space-x-8 md:mt-0 md:border-0 md:bg-white dark:bg-gray-800 md:dark:bg-gray-900 dark:border-gray-700">
<li>
<SignoutButton />
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
);
};
export default CustomAppbar;
Note that this is not a client component. We are basically telling NextJs that it can be rendered on the server side since we have encapsulated the signout logic to the SignoutButton component. This provides us with an island (the signout button) where users can interact with the site. While the rest of the component can be crawled since its server is rendered.
I have to credit Flowbite for the Appbar above. If you haven’t used them before, I’d highly encourage you check them out.
Example 1
In the first example, we will interact with the Greeting Contract which has been deployed on the Polygon Mumbai Testnet. The code for this is inside the example1 folder inside components. The overall look of it will be similar to the image below. We will abstract away the logic into smaller, focused client components. These components (called GreetingGetter and GreetingSetter) will be lazily loaded into the GreetingCard component. The Code for the GreetingCard component is shown below.
import React from "react";
import Card from "../ui/Card";
import dynamic from "next/dynamic";
const GreetingGetter = dynamic(
() => import("./GreetingGetter"),
{ ssr: false }
)
const GreetingSetter = dynamic(
() => import("./GreetingSetter"),
{ ssr: false }
)
export const GreetingCard = () => {
return (
<Card>
<h3 className="text-xl font-bold text-gray-400">Example 1:</h3>
<GreetingGetter />
<GreetingSetter />
</Card>
);
};
Lines 5-13 are of interest in the above code section. This is where we use the dynamic imports for the components. We tell NextJs to not load these components on the server (ssr:false). This is why, these components will be loaded when the page is first loaded on the client. This is why there would be some delay.
Get Greeting
First up, let’s have the getter component. Here, we will use the long way to do contract reads. We will fetch the Public Client from Viem and then make a contract read call. Normally, you’d do this with one step using the useContractRead() hook from Wagmi. But this method will allow you to find some similarities between Ethers and Viem. The code for the component is shown below:
"use client";
import React from "react";
import { usePublicClient } from "wagmi";
import greeterAbi from "@/blockchain/greeter_abi.json";
import StyledButton from "../ui/StyledButton";
const GreetingGetter = () => {
const [greeting, setGreeting] = React.useState<string>();
const publicClient = usePublicClient();
const greetingGet = async () => {
const data = await publicClient.readContract({
address: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GREETING_CONTRACT,
abi: greeterAbi,
functionName: "greeting",
});
setGreeting(data as string);
};
return (
<div className="flex flex-col justify-center items-center bg-black p-4 rounded-lg border-2 border-gray-600 my-4">
<h4 className="text-xl font-semibold text-gray-400">Get Greeting</h4>
<p className="block w-full my-4 text-gray-200">
<b>Greeting:</b> {greeting}
</p>
<StyledButton onClick={greetingGet} color="green">
Get
</StyledButton>
</div>
);
};
export default GreetingGetter;
At line 8 we declare a state variable which will contain the Greeting. Now we could have easily created a custom hook which would have used useState, useEffect from React and usePublicClient() hook from Wagmi but that would defeat the purpose.
We fetch the pubic client using the usePublicClient() hook. Since we have made our config “chain-aware” and also because we are only using Polygon Mumbai Testnet, we do not need to pass in the chainId to force the Public Client to connect to a specific chain.
We have the greetingGet function that helps us fetch the value of the greeting variable in the smart contract. We pass in the address, the ABI and the function name to invoke the readContract() method of the public client.
Keep in mind, the data returned here will be a Big Number if its an integer. However, in our case, data is just a string. We need to additionally typecast it to string using data as string while setting the greeting state variable in our component.
Once something clicks on the Get Button, we fetch the greeting.
Set Greeting
GreetingSetter component is a bit more interesting. When WalletConnect connects to our wallet, it fetches a list of accounts from it. We can use the account with which we have signed the message with useAccount() hook of Wagmi. This is needed when invoking a write function on the smart contract. Like the code above, we could have used a wallet client (Viem counterpart of signer from Ethers) and invoked the setter. But as shown in the code below, we use Idiomatic React.
"use client";
import React from "react";
import { useAccount, useContractWrite } from "wagmi";
import greeterAbi from "@/blockchain/greeter_abi.json";
import StyledButton from "../ui/StyledButton";
const GreetingSetter = () => {
const { address: account } = useAccount();
const { write } = useContractWrite({
address: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GREETING_CONTRACT,
abi: greeterAbi,
functionName: "setGreetings",
account,
});
const greeting = React.useRef<HTMLInputElement | null>(null);
const [value, setValue] = React.useState<string>("");
const handleChange = (e: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setValue(e.target.value);
};
const handleSet = async () => {
write({
args: [greeting.current?.value],
});
};
return (
<div className="flex flex-col justify-center items-center bg-black p-4 rounded-lg border-2 border-gray-600 my-4">
<h4 className="text-xl font-semibold text-gray-400">Set Greeting</h4>
<input
className=" block w-full p-2.5 bg-black rounded-lg border border-gray-600 placeholder-gray-400 text-gray-500 focus:ring-blue-500 focus:border-blue-500 my-4"
ref={greeting}
value={value}
onChange={handleChange}
/>
<StyledButton color="pink" onClick={handleSet}>
Set
</StyledButton>
</div>
);
};
export default GreetingSetter;
In the code above, at line 8, we fetch the address which is connected to our NextJs App (renaming it to account). Next, we use the useContractWrite() hook from Wagmi. This hook is a wrapper around the WalletClient’s writeContract() method in Viem.
You might be confused here. How can we pass in the data beforehand and invoke the write method when we don’t have the greeting to set? Well that a natural way to think. The thing is, we pass in the bare minimum to initialize the hook between lines 9 and 14. The setGreetings on our smart contract is not invoked until we pass in our new greeting using the write method which the useContractWrite() Wagmi hook returns.
Lines 16 to 20 are just simple React way to handle User Input. When the use clicks on the Set Button, the handleSet() method is invoked which in turn creates a transaction by passing in the arguments to the function on the smart contract we had mentioned when initializing the contract write hook.
This will create a Metamask transaction. When the transaction succeeds, the user will have to click on Get button in the GreetingGetter component to fetch the new greeting.
This completes the first example. You might be thinking at this point, why not have the greeting automatically be updated inside our NextJs 13 app when the transaction succeeds? That would mean a smoother UI flow as well. In the next section, we will look into that. We will cover how to listen to a submitted transaction using Wagmi and Viem and based on transaction status, act inside our application.
Example 2
Now example 2 is a bit more complicated than the example above. In this example, we will interact with an NFT contract. We will fetch the balance of the address we are using to connect to our Next app and also use Wagmi and Viem hooks to mint a new NFT. I have already deployed a smart contract for this on Polygon Mumbai Testnet just like the example above. You can find the addresses of both the contract in the README.md inside the smart_contract directory. The code for the NFTCard.tsx is simple enough as shown below.
import dynamic from "next/dynamic";
import React from "react";
import Card from "../ui/Card";
const MintSection = dynamic(
() => import("./MintSection"),
{ ssr: false }
)
export const NFTCard = () => {
return (
<Card>
<h3 className="text-xl font-bold text-gray-400">Example 2:</h3>
<MintSection />
</Card>
);
};
In the code above, we just import the Client component ‘MintSection` as a dynamic import. That’s all really.
Fetch Balance
In the first part, we need to fetch the user balance. This is something that will be done as the component loads in. The code below does precisely that:
const { address } = useAccount();
const { data, isSuccess, isLoading, refetch } = useContractRead({
address: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT,
abi: nftAbi,
functionName: "balanceOf",
args: [address],
});
We use the useAccount() hook from Wagmi to get the wallet address connected to our Next App. Then we use the useContractRead() hook to invoke the balanceOf function on our smart contract. Notice how we provide the arguments (our wallet address) in the args array. There are two things to note here:
If you want to invoke multiple read-type functions on a smart contract all at once, you would use the
useContractReads()hooks. This is different from theuseContractInifiteReads()which allows for fetching repeatedly kind of thing (ideal for fetching total value locked or any other live data).The
useContractReact()hook provides arefetch()method as shown above. This can be invoked to refresh the value ofdatamanually.
The data will be a bignumber-ish value in our case. We will have to typecast it to string when using in our component to show the balance.
Mint an NFT
Next, we move on to minting a new NFT. This is interesting because it showcases how versatile using Wagmi hooks is. The code below contains the logic for minting an NFT using Wagmi hooks.
const { data: writeData, write } = useContractWrite({
address: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT,
abi: nftAbi,
functionName: "safeMint",
account: address,
});
useWaitForTransaction({
hash: writeData?.hash,
onSuccess() {
refetch();
},
});
const handleMint = async () => {
write({
args: [address],
});
};
As in example 1, we use useContractWrite() hook from Wagmi. But here we go a step further and watch the transaction. The data returned from useContractWrite() will contain the hash of the generated transaction. We pass that onto useWaitForTransaction() hook. This hook returns the Transaction Receipt as data. Since we do not need that here we do not consider the return values.
We provide the generated transaction hash to the useWaitForTransaction() Wagmi Hook. Then we use the onSuccess() callback to specify what to do if the transaction succeeds. A general doubt here can be “how can we pass the transaction hash in the hook until the transaction is created inside the handleMint() method?”. This is a very good doubt. Turns out, this hook does not run till it gets a valid hash. So, when we submit our transaction and generate a hash, this hook will automatically run and monitor the transaction.
It may also be noted that this hook also has callbacks relating to other transaction states. One can utilize the onError() callback in the useWaitForTransaction() hook to act to transaction failure. Alternatively, there is also the onSettled() callback. This callback is used when the transaction has either failed or succeeded (but in all forms, has been settled). I would really encourage you to refer to the hook’s documentation for more information.
In our case, we make sure that if the transaction we are watching succeeds, then the refetch() method provided by useContractRead() hook is run. This will update the balance shown in our component. The flow thus becomes –
The user clicks on the Mint button which invokes the
handleMint()function. This function generates a transaction to invoke thesafeMint()function in our smart contract.The
useWaitForTransaction()hook watches the transaction.When the transaction succeeds, the
refetch()method is invoked.The new balance is updated in our component.
Assembling into MintCard Component
Now, we need to put the above 2 subsections together. The following code section shows the contents of the MintSection.tsx in entirety.
"use client";
import React from "react";
import {
useAccount,
useContractRead,
useContractWrite,
useWaitForTransaction,
} from "wagmi";
import nftAbi from "@/blockchain/nft_abi.json";
import StyledButton from "../ui/StyledButton";
const MintSection = () => {
const { address } = useAccount();
const { data, isSuccess, isLoading, refetch } = useContractRead({
address: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT,
abi: nftAbi,
functionName: "balanceOf",
args: [address],
});
const { data: writeData, write } = useContractWrite({
address: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_NFT_CONTRACT,
abi: nftAbi,
functionName: "safeMint",
account: address,
});
useWaitForTransaction({
hash: writeData?.hash,
onSuccess() {
refetch();
},
});
const handleMint = async () => {
write({
args: [address],
});
};
return (
<div className="h-full mt-4 lg:flex lg:flex-col lg:justify-evenly lg:items-center">
<p>
You are signed in as{" "}
<span className="font-bold tracking-tight">
{address?.slice(0, 5)}...
{address?.slice(address.length - 5, address.length)}
</span>
.
</p>
<p>
Your Balance:{" "}
{isLoading && <span className="font-semibold">loading...</span>}
{isSuccess && (data as any).toString()}
</p>
<div className="flex justify-center items-center mt-3">
<StyledButton color="pink" onClick={handleMint}>
Mint
</StyledButton>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default MintSection;
Apart from the codes discussed in the above 2 sub-sections, nothing else is worthy of discussion in the code above. This MintCard component handles the entire minting logic. It might have been better to split this in a manner we had split the Greeting components. In fact, I would recommend you do that in your case. Would help adherence to SOLID principles.
Mecha is Assembled
In this section, we put all the components into the hidden page. Our page.tsx inside the hidden directory should look something just like the code below.
import React from "react";
import CustomAppbar from "../components/CustomAppbar";
import { GreetingCard } from "../components/example1";
import { NFTCard } from "../components/example2";
const HiddenPage = () => {
return (
<div className="min-h-screen">
<CustomAppbar />
<main className="container mx-auto flex flex-col justify-center items-center">
<h1 className="text-5xl tracking-tight font-extrabold text-gray-300">
Yohoo!!
</h1>
<h2 className="text-3xl text-gray-500">
You have <span className="font-bold">Started</span>.
</h2>
<p className="">
You have been signed in{" "}
<span className="font-semibold text-green-400 text-xl">
successfully
</span>
!
</p>
<div className="grid grid-cols-1 lg:grid-cols-2 gap-4">
<GreetingCard />
<NFTCard />
</div>
</main>
</div>
);
};
export default HiddenPage;
We have our custom App bar followed by the main section (line 11-29). This section shows some information to the user. We use the grid layout of Tailwind to make things a little responsive between lines 25 and 28. And that’s it! Our mini-project is ready. Run npm run dev and you should see the culmination of our three-part series on Next Auth and NextJS 13 in Web3.
Conclusion
This brings us to the end of our Three-Part series. In this series, we tried to answer the following questions:
How to use NextJs 13 in a Web3 project?
How to use WalletConnect, Wagmi and Viem in NextJs 13?
How to integrate WalletConnect with Next Auth?
I hope this helped you understand the concepts. If you have anything to share, feel free to open a discussion below. Until next time, don’t stop building awesome things in Web3 and WAGMI!
